
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, ITIL change management stands as a guardian, ensuring that changes to IT systems enhance capability without disrupting service.
Imagine orchestrating a flawless ballet of code and hardware, where each move, however small or substantial, is methodically planned, reviewed, and executed to maintain the delicate balance of business operations. ITIL change management isn’t just about avoiding disasters; it’s about elevating performance.
As organizations grow and adapt, the importance of managing technical change seamlessly becomes paramount. ITIL change management is a critical process within IT Service Management (ITSM) that aims to control and manage the lifecycle of all changes to IT services, infrastructure, applications, and other configuration items. It aims to efficiently and effectively manage changes to avoid disruptions, minimize risks, and ensure smooth operations.
The three main types of ITIL change management are (1) Standard, (2) Normal, and (3) Emergency, categorized based on risk and complexity. ITIL V3 and ITIL V4 are different versions of the ITIL framework. While ITIL V3 focuses on controlling the lifecycle of all changes, ITIL V4 addresses modern complexities and emphasizes value co-creation.
The ITIL change management process flow consists of five key stages:
(1) Request for Change (RFC), (2) Change Evaluation, (3) Change Approval, (4) Change Implementation, and (5) Change Review and Closure.
Each stage involves specific activities and interactions between stakeholders to ensure controlled and efficient change management.
ITIL maturity model, consisting of 5 levels, is used to assess an organization’s level of maturity in implementing ITIL change management best practices such as establishing a formal change management process, categorizing and prioritizing changes, building a Change Advisory Board (CAB), and maintaining a centralized change record.
To further facilitate change management, we’ve provided you with ITIL template resources, such as ITIL change management process template, ITIL change request template, ITIL incident report template, and IT change management policy template that you can utilize in your organization.
Additionally, using online ITIL change management tools and ITIL change management software, can help streamline change efforts, track metrics, and align with industry-standard methodologies.

ITIL Change Management Summary
Detailed Section – Overview
We hope you found the summary section above helpful. If interested in reading further, see the detailed sections below which provide you with a comprehensive overview of ITIL change management, guiding you through everything you need to know – from change management definition ITIL to ITIL change management types.
In addition to that, we will delve into the ITIL framework for change management, discussing the scope of change management and the ITIL maturity model. But that’s not all! We’ll also take an in-depth look at the ITIL change management process. This will include detailed steps such as Request for Change (RFC), Change Evaluation, Approval, Implementation, Review, and Closure.
For those who prefer a visual approach, we’ve included a helpful ITIL Change Management Process Flow Diagram to enhance your understanding. To make your journey even more convenient, we have provided you with essential downloadable ITIL change management tools and templates and IT change management best practices.
Our goal is to equip you with all the necessary knowledge and resources to understand and apply ITIL change management in your IT projects. So, by the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of ITIL change management and how it can be practically implemented in your projects.

Change Management ITIL – 2024 Guide
Get ready to learn everything you must know about change management for IT sector. For those of you looking for free ITIL template resources, ITIL incident report template, samples, and checklists that can be utilized to implement and streamline their change management processes, you’re at the right place.
If you’re ready to learn about change management for IT, see the Table of Contents below for a detailed step-by-step overview.

DETAILED SECTION
If you’re eager to learn more about ITIL, proceed to our detailed sections below that provide a detailed overview.
Table of Contents: Guide on IT Change Management Best Practices
Keep on scrolling down this page to read each section or click any link below to go directly to that section.
In order to understand the full scope of change management ITIL we need to start with the ITIL change management definition.
What is Change Management ITIL? | ITIL Change Management Definition
In the dynamic world of Information Technology, changes are inevitable.
However, managing these changes efficiently and effectively is crucial to avoid disruptions, minimize risks, and ensure seamless operations.
This is where ITIL change management comes into play.
ITIL change management is a fundamental process within IT Service Management (ITSM) that aims to control and manage the lifecycle of all changes to IT services, infrastructure, applications, and other configuration items (CIs).
What is the ITIL change definition?
Change management definition ITIL refers to the addition, modification, or removal of any hardware, software, infrastructure, network, or other IT component that could have an impact on IT services or the business as a whole.
This ITIL change definition emphasizes the importance of considering all aspects of the IT environment when managing changes to ensure that business continuity and service quality are not compromised.
ITIL change can range from minor routine updates to major system overhauls. With ITIL change management definition laid out, it’s time to define different types of change management in ITIL.

Do you need more information about ITIL 4 overview assessment or ITIL V4 change management in general? Please reach out and let us know.
ITIL Change Management Types
There are three main types of change management in ITIL that organizations can use to manage changes within their IT environment. These ITIL change management types are defined based on the level of risk and complexity associated with the changes being implemented.
The three types of change management in ITIL are:
Let’s take a look at each of the ITIL change management types to get a better understanding of what they’re about.
1. ITIL Standard Change Management – ITIL Standard Change Examples
ITIL standard change management incorporates pre-authorized and low-risk changes that are frequently occurring and well understood. ITIL standard change is typically of low impact and is considered routine and straightforward.

Types of Change Management in ITIL
ITIL standard change examples include:
Since these ITIL standard change examples are pre-approved and well-documented, they do not require the same level of scrutiny and formal approval as other types of changes.
ITIL standard change management allows organizations to streamline and expedite the implementation of routine changes while maintaining control and consistency.
2. ITIL Normal Change Management
Normal change ITIL management is more significant in terms of risk and impact compared to standard change but is still well-defined and has known outcomes.
Normal change ITIL involves more complexity and may require formal approval and assessment by the Change Advisory Board (CAB) or ITIL change manager. ITIL normal change management often requires a detailed change plan, ITIL change management plan template, and risk analysis before implementation.
ITIL normal change management strikes a balance between efficiently implementing changes and minimizing risks. Specific examples of changes that would fall under normal change ITIL management are:
These IT normal change examples illustrate changes that are more significant in scope, complexity, and potential impact compared to standard changes.
Overall, ITIL normal change management ensures that these changes are carefully evaluated and managed to minimize disruptions and maximize successful outcomes. Looking for an IT change management process template? Get in further down in this comprehensive guide on change management for IT.

3. ITIL Emergency Change Management
ITIL emergency change management changes are unplanned and urgent changes that need to be implemented immediately to address critical situations, such as system failures or security incidents.
These changes carry a higher level of risk and can be disruptive to IT services if not managed effectively. Emergency changes are implemented as quickly as possible to restore service functionality or mitigate threats.

Emergency IT Change Management System
Here are some specific examples of changes that would fall under ITIL emergency change management:
By categorizing changes into these three ITIL change management types, ITIL helps organizations apply appropriate levels of control, review, and approval based on the risks and impacts of the changes.
Now that we have all the types of change management in ITIL covered, we’ll get a good grasp of ITIL framework change management. Next, we’ll move to the IT change management process.
ITIL Framework Change Management
When delving into the world of ITIL change management, you might encounter a plethora of information. This is due to the immense popularity of the ITIL change management framework and the significance of both ITIL v3 change management and the newly released ITIL 4 change management process.
The ITIL change management framework encompasses the full lifecycle of information technology management, with the ITIL change process being a vital part of it.
Change Management Scope
Change management is the process of controlling the lifecycle of all changes to an IT service or system, ensuring that only approved and authorized changes are implemented.
The change management scope typically includes:
Incident, Change, and Problem Management | ITIL Incident Problem Change
Incident, change, and problem management are 3 processes that are integral parts of the ITIL framework and work closely together to ensure the smooth operation and improvement of IT services.
Incident Management | Incident, Change, and Problem Management: Incident management focuses on restoring normal service operations as quickly as possible following any disruption.
It involves logging, categorizing, prioritizing, and resolving incidents, thereby minimizing the impact on business operations. The best way to capture ITIL incident problem change is with the help of the ITIL incident report template.
Keep on reading to find our copy of ITIL incident report template further down in this article.
Change Management | Incident, Change, and Problem Management: As discussed earlier, change management is responsible for controlling the lifecycle of all changes. It evaluates and approves changes to minimize risk and potential disruptions to IT services and the business.
Problem Management| Incident, Change, and Problem Management: Problem Management aims to identify and address the root causes of incidents and recurring problems. It involves analyzing incident data, conducting root cause analysis, and initiating corrective actions to prevent future incidents from occurring.
ITIL Maturity Model – ITIL Change Management Framework
The ITIL maturity model is a framework that helps organizations assess their level of maturity in implementing ITIL change management best practices.
It provides a structured approach to understanding an organization’s current state and identifies areas for improvement. The ITIL maturity model typically consists of multiple levels or stages, each representing different levels of process maturity.
The common levels in the ITIL Maturity Model are:
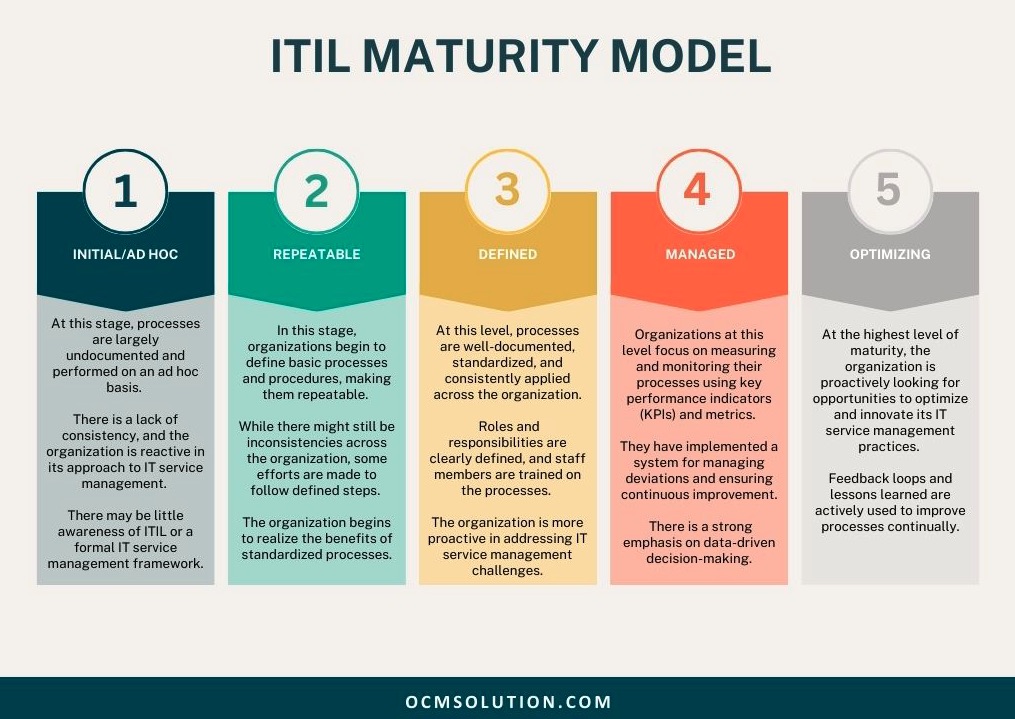
ITIL Maturity Model
The ITIL maturity model serves as a benchmark to help organizations understand where they stand in their ITIL journey and guide them in setting realistic improvement goals.
Advancing through the maturity levels typically requires commitment from top management, adequate resources, training, and a culture of continuous improvement.
The goal is to progress from an ad hoc and reactive approach to a more mature, proactive, and efficient IT service management framework that aligns with business objectives and enhances customer satisfaction. Next, we’ll discuss the difference between change management ITIL v3 and change enablement ITIL 4.
Let’s get right into it!
Do you have any questions about change model ITIL or ITIL change management examples? Don’t hesitate to reach out and let us know.
What is Change Management ITIL V3?
Change Management ITIL V3 refers to one of the core processes within the IT change management framework. ITIL V3 change management is ITIL framework change management that provides ITIL change management best practices for managing IT services and processes to deliver value to customers and align IT with business needs.
Change Management ITIL V3 Process
The change management ITIL V3 process focuses on controlling the lifecycle of all changes to IT services and infrastructure. Its primary objective is to ensure that changes are properly evaluated, authorized, prioritized, and implemented with minimal disruption to IT services and business operations.
Key Components of ITIL V3 Change Management
This IT change management policy ensures that all stakeholders follow a standardized and consistent approach to change management.
Benefits of ITIL V3 Change Management Include:
In summary, ITIL V3 change management is a critical process that enables organizations to manage changes effectively, reduce risks, and ensure the stable and efficient delivery of IT services to meet business objectives.
What is Change Management ITIL V4?
Change Management ITIL V4 is a fundamental practice that remains essential in guiding organizations through the process of planning, evaluating, and implementing changes to IT services and related components.
ITIL4 change management is the latest evolution of the IT change management framework, designed to address the modern complexities of IT service delivery and value co-creation in a dynamic business environment.
Key Characteristics of ITIL V4 Change Management
ITIL V4 change enablement terminology emphasizes the proactive nature of change, encouraging organizations to embrace change as an opportunity for improvement and innovation rather than merely reacting to it as a disruptive force.

ITIL4 Change Management
What You Need to Know About Change Enablement ITIL 4
Change Enablement in ITIL 4 refers to a crucial set of practices and principles that empower organizations to embrace change as a positive force and enhance their ability to deliver value to customers and stakeholders.
It is one of the key components within the ITIL framework change management, focusing on fostering a culture of agility, innovation, and continual improvement.
⋅ Embracing Change as an Opportunity
ITIL change enablement emphasizes the importance of viewing change not just as a disruption but as an opportunity for growth and improvement.
⋅ Flexibility and Adaptability:
ITIL change enablement encourages organizations to be flexible and open to new ideas, allowing them to respond quickly to emerging opportunities and challenges.
⋅ Collaboration and Communication:
It involves engaging employees, customers, partners, and other key players to foster a shared understanding of the vision and goals behind the changes.
⋅ Change Management Process:
Change enablement ITIL 4 is a critical component of Service Management Practices. It includes the change management process, which guides the assessment, authorization, and implementation of changes to IT services and related components.
⋅ Co-Creation of Value:
Change Enablement aligns with the core principle of ITIL 4 – value co-creation. By involving all relevant parties in the change process, organizations can collaboratively create value for customers, ensuring that changes are designed to meet their needs and expectations.
⋅ Continuous Improvement:
ITIL change enablement fosters a culture of continual improvement by encouraging organizations to learn from each change initiative.
⋅ Innovation and Creativity:
ITIL V4 change enablement promotes innovation and creativity by creating an environment where new ideas are welcomed and experimentation is encouraged.
⋅ Risk Management:
While encouraging change, change enablement ITIL 4 also emphasizes the importance of managing risks associated with change.
⋅ Leadership Support:
For effective change enablement, strong leadership support is essential as they play a key role in the change.
Let’s now simplify the concept of ITIL and change management with an overview of the ITIL change management workflow.
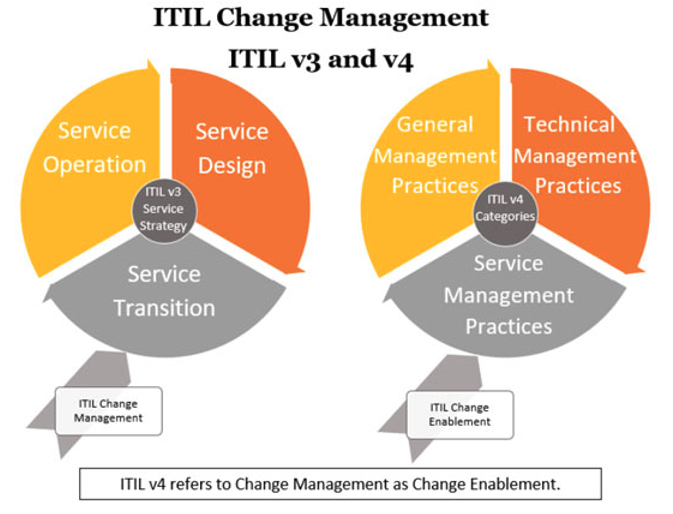
ITIL V4 Change Management
Do you have any questions about ITIL 4 overview assessment or ITIL change and release management? Please reach out and let us know. We’ll love to hear from you.
What is ITIL Change Management Process? | How Does Change Management for IT Work?
The ITIL change management process is a systematic approach to controlling and managing changes to IT services, infrastructure, applications, and other configuration items (CIs) within an organization.
ITIL change process aims to ensure that any IT change instances are implemented with minimal risk and disruption to IT operations and business services.
The ITIL change management process flow typically involves the following key stages:
In the sections below we’ll go over each of the stages of the ITIL change process along with ITIL change management examples.

1. Request for Change (RFC) – ITIL Change Management Process Flow
The change process ITIL begins with the submission of a formal Request for Change (RFC).
What is the ITIL change request definition?
ITIL change request definition refers to a documented request that outlines the proposed change, including its:
The request for ITIL change can be initiated by various stakeholders, including end-users, IT staff, or management.
The change request is a crucial starting point in the IT change management process flow, as it initiates the evaluation, approval, and implementation of the proposed change.

Request for Change (RFC) – Change Management in IT Projects
The change process ITIL request and ITIL change request template typically include the following key information:
The information provided in the change request is critical for the evaluation and decision-making processes during the IT change management process flow.
By using ITIL change management process document or documenting and evaluating change requests, organizations can make informed decisions, minimize risks, and improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of their ITIL change management process and practices.
Looking for an IT change management form template for request? Read on, and find your copy of the ITIL change request template/ IT change management form template further down in this article.

2. Change Evaluation – ITIL Change Management Process Flow
Once the Request for Change (RFC) is submitted, the ITIL change manager and the team kick off the crucial phase of change evaluation.
This stage is pivotal in the IT change management process as it involves a comprehensive ITIL assessment of the proposed change’s viability and potential impact on the organization’s IT environment.
The goal is to make informed decisions regarding whether to approve, modify, or reject the change based on its feasibility, risks, and expected benefits.
⋅ Thorough Analysis of Feasibility: During the change evaluation, the ITIL change management team thoroughly analyzes the proposed change to determine its feasibility.
This involves scrutinizing various aspects, such as:
The ITIL change management team assesses whether the required resources and capabilities are available to implement the ITIL change successfully.
⋅ Identification and Analysis of Risks: Another critical aspect of the change evaluation is the identification and analysis of potential risks associated with the proposed IT change.
The ITIL change management team considers both technical and business-related risks, including the:
By understanding the risks, the change management ITIL team can develop risk mitigation strategies to minimize the impact and likelihood of negative consequences.
⋅ Assessment of Expected Benefits: Alongside evaluating risks, the change management ITIL team also assesses the expected benefits of the proposed change.
This involves understanding how the change aligns with business objectives and the potential positive outcomes it can deliver, such as:
This evaluation helps to balance the risks with the potential rewards and supports decision-making in the best interest of the organization.
⋅ Impact Analysis on IT Services and Infrastructure: Understanding the impact of change management for IT services, infrastructure, resources, and processes is crucial for effective change management.
The change management ITIL team carefully evaluates the change’s consequences on:
This analysis helps in identifying any potential conflicts or dependencies that may arise due to the IT change process.
⋅ Documentation and Reporting: Throughout the change evaluation process, the change manager ITIL and the team meticulously document their findings, assessments, and recommendations in the ITIL change management process document.
This documentation is vital for transparency, accountability, and future reference.
It provides a clear record of the evaluation ITIL change management process flow, the rationale behind the decision, and any actions taken to address identified risks or concerns.
⋅ Collaboration and Consultation: Change evaluation often involves collaboration and consultation with various stakeholders, including:
Engaging stakeholders and seeking their input ensures a well-rounded ITIL assessment of the change’s impact and encourages buy-in from those who will be affected by the change.
Do you have any input on IT change management examples that we haven’t mentioned? If so, don’t hesitate to get in touch.
3. Change Approval – IT Change Management Process Flow
After the change evaluation, the RFC is reviewed by the Change Advisory Board (CAB) or change manager ITIL.
The Change Approval phase is a critical checkpoint in the ITIL change management process.
The CAB’s role is to assess the change’s potential impact on the organization as a whole and make an informed decision about whether to approve, reject, or modify the change.
Once a decision is made, the CAB records its conclusions and the rationale behind the decision.
This documentation ensures transparency and serves as a historical record for future reference.
If the change is approved, the stakeholders involved are informed, and preparations for the change implementation phase are initiated.
The CAB meetings also serve as a platform for continuous improvement.
Any lessons learned or insights gained from past changes are discussed, allowing the organization to refine its IT change management practices and optimize future change initiatives.
4. Change Implementation – ITIL Change Management Process low
Once the IT change management process is approved, the implementation phase begins.
The Change Implementation phase is a critical stage in the change Management ITIL.
After receiving approval from the Change Advisory Board (CAB) or ITIL change manager, the organization proceeds with the actual execution of the approved change.
To ensure a smooth and controlled implementation with minimal disruption to IT services and business operations, the change implementation phase in change management for IT requires:
A detailed implementation plan is developed, outlining the necessary steps, resources, and timelines.
⋅ Detailed Implementation Planning: Effective implementation begins with a detailed and well-structured IT change management plan.
The ITIL change management team, along with relevant stakeholders, develops a comprehensive implementation plan and ITIL change management plan template that outline the specific steps, tasks, and activities required to execute the change successfully.
The IT change management plan template also includes a clear timeline, resource allocation, and responsibilities assigned to each team member involved in the implementation.
⋅ Coordinated Execution: During implementation, close coordination among different teams is crucial.
The ITIL change management team collaborates with IT operations, application owners, support teams, and other stakeholders to ensure a seamless transition.
All teams must be aware of their roles and responsibilities to perform their tasks effectively.
⋅ Change Control: To maintain control during implementation, the ITIL change management team follows strict change control procedures.
Change control procedures include:
⋅ Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Clear and timely communication is essential throughout the implementation phase.
The ITIL change management team communicates the details of the change its expected impact, and any temporary disruptions to relevant stakeholders, including end-users, customers, and business units.
Regular status updates keep all parties informed about the progress and mitigate concerns.
⋅ Backout Plan and Contingency Measures: Despite careful planning, there is always a possibility of unforeseen issues during implementation.
To address this, a backout plan is prepared in advance. The backout plan outlines the steps to revert the changes and return the system to its previous state if the implementation encounters significant problems.
Additionally, contingency measures are put in place to handle any unexpected events effectively.
⋅ Testing and Validation: Before implementing changes in the live environment, testing and validation are conducted in a controlled test environment. This helps identify and rectify any issues or defects before they impact production systems
⋅ Post-Implementation Review: After the change management for IT is successfully implemented, a post-implementation review is conducted to assess the effectiveness of the change and its impact on IT services and business operations.
The review of change management for IT includes evaluating whether the change has achieved its intended outcomes and if any lessons can be learned for future changes.

5. Change Review and Closure – Change Management ITIL Process
The Change Review and Closure phase is the final step in the ITIL change process.
After the successful implementation of the change management in IT, the change management team conducts a comprehensive review to assess the outcomes and impacts of the change.
This review is essential for learning from the change process, identifying areas of improvement, and ensuring that the organization continues to refine its it change management procedure.
⋅ Post-Implementation Evaluation: The post-implementation review is a systematic evaluation of the change’s success and its impact on the IT environment and business operations.
This evaluation considers whether the change achieved its intended objectives and if it delivered the expected benefits. It also examines whether any unforeseen issues or challenges arose during implementation and how they were addressed.
⋅ ITIL Change Management Metrics: To gauge the effectiveness of the change, the change management team measures key performance indicators (KPIs) established during the change evaluation phase.
These change control metrics may include:
Analyzing these ITIL change management KPIs helps the organization understand the overall impact and effectiveness of the change.

ITIL Change Management Metrics – KPI of Change Management in ITIL
⋅ Lessons Learned: The post-implementation review captures valuable insights and lessons learned from the ITIL change process flow.
The ITIL change management team identifies what worked well during the implementation and what could be improved in future change initiatives.
These lessons are documented and shared within the organization to enhance ITIL change management best practices and avoid repeating the same mistakes.
⋅ Documentation Update: Once the post-implementation review is complete, relevant documentation is updated to reflect the changes made during the implementation.
This documentation includes:
Keeping the documentation accurate and up-to-date ensures that future stakeholders have access to a comprehensive and reliable historical record.
⋅ Change Closure: With the change deemed successful and all documentation updated, the change is officially closed in the change management system.
The change status is updated to reflect its closure, and any associated records and tasks are appropriately closed.
Closure signifies the end of the formal change process and the transition to operational activities.
⋅ Continuous Improvement: The insights gathered from the post-implementation review feed into the organization’s continuous improvement efforts.
The change management ITIL team analyzes the review results and identifies opportunities for enhancing change management processes and practices.
Implementing improvements based on these findings strengthens the organization’s change capability and ensures a more efficient and effective approach to managing future changes.
As demonstrated, the change process ITIL focuses on balancing the need for change with the need to minimize risks and disruptions.
It ensures that changes are thoroughly assessed, planned, and executed while keeping stakeholders informed and involved throughout the entire process.
Next, let’s get a visual presentation of the ITIL change management process.
Do you have any questions or input about the ITIL change and release management or ITIL change management examples we provided? Just reach out and let us know.
ITIL Change Management Process Flow Diagram | How to Utilize the Diagram
An ITIL change management process flow diagram provides a visual representation of the step-by-step sequence of activities involved in managing changes within an organization’s IT environment.
The change management process flow diagram illustrates the key stages and interactions between stakeholders during the change management process.
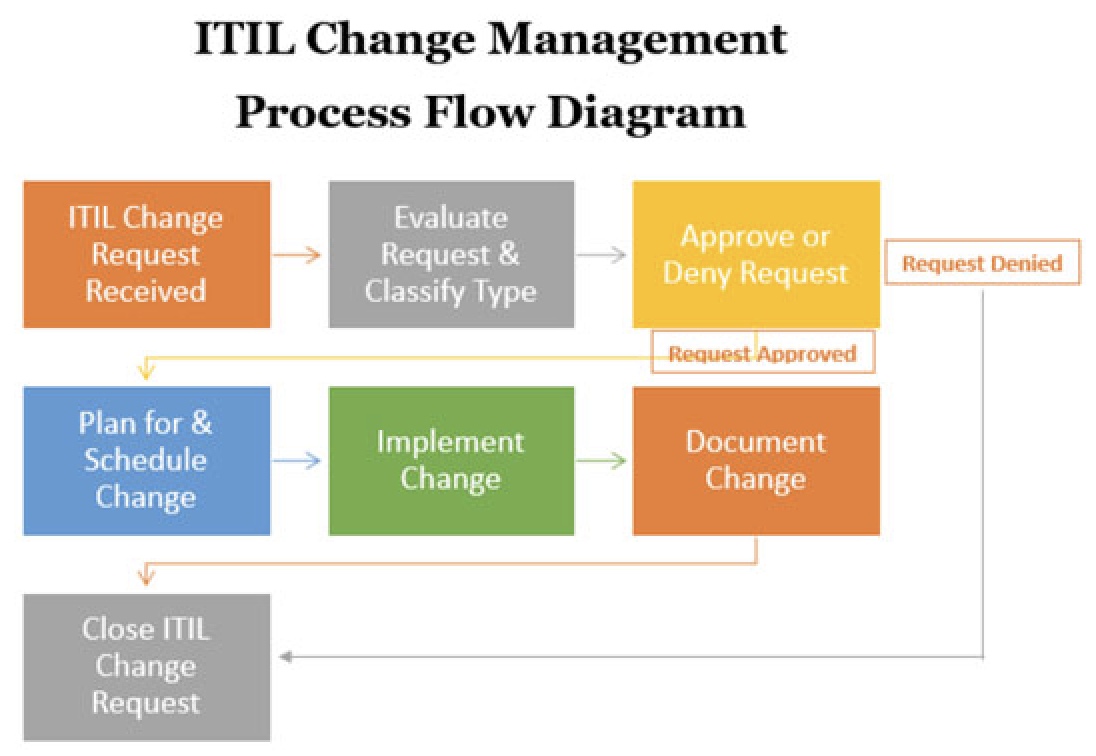
ITIL Change Management Process Flow Diagram
Using the ITIL change management process flow diagram can help organizations streamline their change management practices and ensure a controlled and efficient approach to managing changes in the IT environment.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to utilize the above ITIL change management process flow diagram:
Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with the ITIL Change Management Process Flow Diagram
Step 2: Integrate the Diagram into Documentation
Step 3: Use the ITIL Change Management Process Flow Diagram in Training Sessions
Step 4: Guide Request for Change (RFC) Submissions
Step 5: Collaborate in Change Advisory Board (CAB) Meetings
Step 6: Track Progress and Status Updates
Step 7: Conduct Post-Implementation Reviews
Step 8: Optimize the Change Management Process
Step 9: Enhance Compliance and Governance
Step 10: Educate and Align Stakeholders
With that covered, it’s time to look at change management best practices ITIL checklist.
IT Change Management Best Practices | Change Management Best Practices ITIL Checklist
Implementing effective change management practices is essential to ensure that changes are introduced smoothly, with minimal disruption to services and minimal risk to the business.
Here is a checklist of change management best practices ITIL:
Remember that the success of change management in an ITIL environment is not just about following a set of rules but also about fostering a culture of cooperation, risk awareness, and continuous improvement within the organization.
By incorporating these IT change management best practices, IT teams can effectively manage changes, reduce risks, and enhance the overall IT service delivery.
Looking for ITIL template resources? Here we go!
Do you have any further input on change management best practices ITIL? Just reach out and let us know.
ITIL Change Management Template Resources | What ITIL Template Do You Need for Your Project?
We have prepared ITIL template resources that provide valuable ITIL change management tools and guidance for organizations seeking to implement effective IT service management practices.
By utilizing these ITIL template resources, businesses can adopt standardized and structured approaches to incident management, change management, and policy development, leading to improved service delivery and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Click on any of the ITIL template resources to go to that template directly
ITIL Change Management Template / ITIL Change Management Document Template (Overview)
The ITIL change management template or ITIL change management document template provides a comprehensive overview of the organization’s change management process.
ITIL change management document template we’ve provided outlines the steps and procedures for requesting, evaluating, approving, implementing, and reviewing changes.
We hope that this ITIL change management template helps you establish standardized change management practices and ensures compliance with ITIL guidelines.
IT Change Management Form / ITIL Change Request Template
The change management form or ITIL change request template is used to initiate and request changes to IT services or systems.
ITIL change request template includes fields for change details, classification, impact analysis, the reason for change, implementation plan, risk assessment, and approval sections.
This change management form ensures that change requests are properly evaluated, approved, and executed in a controlled manner.
ITIL Incident Report Template
The ITIL incident report template is used to document and manage IT incidents effectively.
ITIL incident report template captures essential details such as incident ID, date, description, impact, affected services or systems, resolution steps, and closure remarks.
ITIL incident report template helps IT teams to record incidents in a structured manner, enabling faster resolution and minimizing disruptions to business operations.
IT Change Management Policy Template / ITIL Change Management Policy Template
The IT change management policy template or ITIL change management policy template is a formal document that defines the rules, principles, and guidelines governing the change management process within the organization.
ITIL change management policy template outlines roles and responsibilities, change categorization, approvals, communication, and escalation procedures.
This IT change management policy template ensures that changes are managed consistently and in alignment with the organization’s goals and objectives.
If you prefer handling change management in IT online, you’ll be interested to learn more about online ITIL change management tools and ITIL change management software in the section below.

Are you looking for some specific IT change management plan template or IT change management plan example? Get in touch and let us know!
Essential IT Change Management Tools | ITIL Change Management Software
Are you embarking on an organizational change project and looking to streamline your change management activities effectively?
ITIL tools are designed to save you time, increase productivity, help you track change control metrics, and align with industry-standard change methodologies, including change management best practices ITIL.
With its comprehensive toolkits, customizable reports, educational resources, and real-time analytics, ITIL change management tools empower change managers to execute successful changes and achieve organizational goals.
Whether you are new to change management or an experienced practitioner, IT change management software caters to your needs, making you more effective in managing your IT change projects.
Conclusion: IT Change Management Best Practices
We hope that this OCM Solution guide on ITIL change management best practices was of great help to you.
One of the key takeaways from this guide is the importance of having a well-defined and documented ITIL change management process.
Implementing a structured and standardized approach allows organizations to handle changes more effectively and consistently, minimizing the potential for disruptions to IT services.
Get on the right track by utilizing IT change management tools such as ITIL change management process template and other ITIL template resources.
We wish you all the best with your change management for IT!
FAQ: Change Management for IT
ITIL change management definition refers to the addition, modification, or removal of any hardware, software, infrastructure, network, or other IT component that could have an impact on IT services or the business as a whole.This change definition ITIL emphasizes the importance of considering all aspects of the IT environment when managing changes to ensure that business continuity and service quality are not compromised.
The three types of change management in ITIL are:
1.ITIL Standard Change Management
2. ITIL Normal Change Management
3. ITIL Emergency Change Management
The change management scope typically includes:
• IT Services and Systems
• Configuration Items (Cis)
• Standard Changes
• Emergency Changes
• Change Windows
• Exclusions
KPI of change management in ITIL may include:
• the success rate of the change,
• the number of incidents or problems encountered post-implementation,
• customer feedback, and
• other relevant data.
Analyzing these ITIL change management KPIs helps the organization understand the overall impact and effectiveness of the change.
Note: Content on OCM Solution's ocmsolution.com website is protected by copyright. Should you have any questions or comments regarding this OCM Solution page, please reach out to Ogbe Airiodion (Change Management Lead) or the OCM Solutions Team today. OCM Solution was previously known as Airiodion Global Services (AGS).
External sources: stock.adobe.com